Lec 1
question about whether technological artifacts have morals imbedded in them or not:
- is technology neutral or malicious/good
- same thing like are guns evil
Theres a lot of power in those who design technology:
- the gadget you are creating → does the responsibility rely on me as the creator or the user.
Kranzberg’s laws:
- technology is neither good nor bad nor neutral:
- tech has social, environmental and human consequences that go far beyond the immediate purposes of the technical devices.
Values, principles, purpose, responsibilities, practices:
- they are all different
- Values - thing that we think are important/strive for
- principles - things if ou believe are high value and do them in practice
- translates into responsibilityies to achieve valuex/expectations
- Practices - similars
Ethical principles typically get put in place way before the law:
- can even lead to new laws
Code of ethics → set of rules about good and bad behaviour To be a licensed profession, you have to abide by a certain set of ethics
Can an action be ethical but illegal or legal but unethical
You need to consider different stakeholders:
- you will impact more ppl than just the target audiencce of products you design.
Beneficence vs Non-Maleficence:
- Do good vs Do no harm
- Do good AND do no harm
Talking about deploying certiain things:
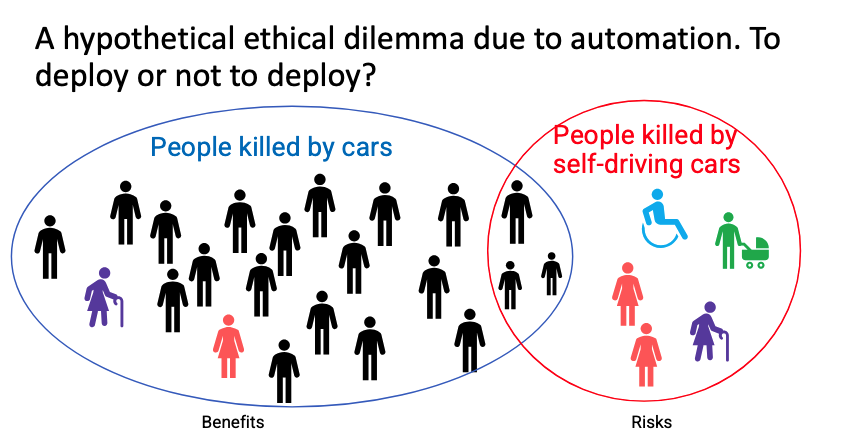
Argument for neutrality: “This moral neutrality is based upon viewing technology purely as a means (providing tools for society to use) with the ends (the actual usage of technology) lying beyond and outside the realm of engineering;
**Automated deicsion making:
- A computerised process that assists/replaces judgement of human decision makers
L2:
Therac 25 Value neutrality thesis:
- whether technology has value assigned to it Why would u trust someone: honest, repuation, loyalty, etc…
FUll automation with full control Tension between automation and human control
- make sure that we can still control the automation → inc case there is an error in the automation
Accountability - 4 barriers:
- problem of many hands
- when u design software, deisgn by many ppl
- problem of bugs
- blaming the computer
- software ownership without liability
ACM principlaes for alogirthmic transparency and accountability
- Awareness
- Access and redress
- Accountability
- Explanation
- Data provenance
- Auditability
- Validation and testing
We want high computer automation and high control → reliable safe and turstowrhty
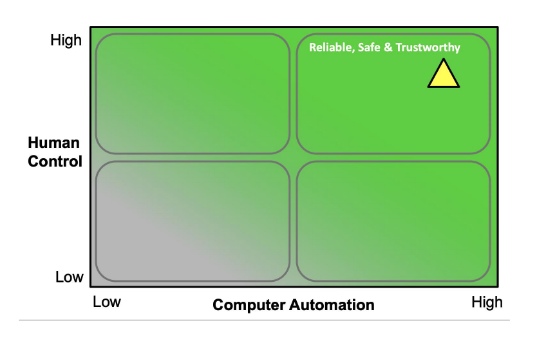
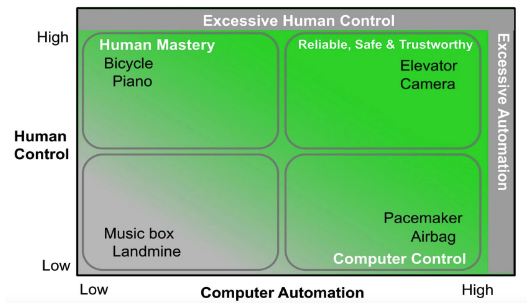
Where does AI ethics sit? Factors:
- human social and envrionmental weelbeing
- reliability
- human -centred values
- transparency and explainability
- fairness
- contestability
- privacy protection and security
- accountbility
AI alignment - design ai to align with the norms and values of your user group in mind
Personas
- models of users
- Rpresent a group of typical users
- can’t be based on a real person
- but can be a ccharacicature that represents the typical person from this model of users
Constructing:
- Identify Behavioural variables
- map interview subject to behavioural variables
- identify significant behaviour patterns
- synthesize characteristics and relevant goals
- check for completeness and redundancy
- Designate persona type
Value sensitive design: an approach that rigorously accountd for human values in the technical design and engineering process
VSD
- Identify the stakeholders
- surfacing of their values through conceptual and empirical investigation
The Judgement Call - The Game
conceptual investigations https://youtu.be/LXqlAXEMGI0
- we should do this in the assignment
- Talk about a scenario
- Ethical Principals
- fairness
- privacy and security
- reliability and safety
- transpareny
- inclusion
- accountability
- Rating
- Ethical Principals
Stakeholders:
- direct - use the technology or being used on them
- indrirect - feel the impact
- sepcial populations - ppl who can’t use t or choose not to
Presnetation of the product:
- who will use it
- what features will it have?
- when will it be used?
- where will it be used?
- why is it useful?
- how will it be used?
Questions to ask when consdidering things:
- who is the most impacted
- what features are the most problematic
- what are teh potenntial harms
Things to consider:
- location data
- e.g pokemon go making spawn places more common in certain areas for certain demogrphics
- displayed info
- facebook manipulating peoples mood by filtering their feeds
- even tho ppl consented to their data being collected, not consented to be experimented on though
- users should consent - e.g be told that it will happen to avoid the observer effectr